
This article is written by Ankita Wani of A.K.K. New Law Academy, Pune, an intern under Legal Vidhiya
ABSTRACT
“Without restoring an ethos of social responsibility, there can be no meaningful and sustained economic recovery.”
-Jaffrey Sachs
Corporate social responsibility has become very important today. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has emerged as a critical aspect of business conduct, reflecting a commitment to ethical, social, and environmental responsibility. In India, the Companies Act, 2013, mandates certain qualifying companies to allocate a percentage of their profits towards CSR activities. This article examines the CSR spending patterns of leading Indian companies, exploring the impact on both national and international fronts.
KEYWORDS
CSR, Corporate Social Responsibility, CSR rules 2014 National CSR initiative, International CSR initiative, Case study, Challenges and recommendations.
INTRODUCTION
The idea of corporate social responsibility is pervasive all over the world and is no different in India. Historically, CSR has been a widespread phenomenon in India. India is one of the countries with one of the richest CSR traditions in the world.
During the COVID-19 situation, when the whole world was caged, frontline workers supplemented public health systems, delivered hygiene kits, and set up temporary isolation facilities. In this context, the contributions of companies such as McDonald’s, Audi, Coca-Cola, Volkswagen and many others are important. Some companies have changed their logos or changed their slogans to spread the message of social distancing.
Reliance Industries, HDFC Bank, Tata Consultancy Services, ONGC, Tata Steel are among the top 5 companies based on their actual CSR spend in India. These five companies account for more than a quarter of total CSR spending.
“Corporate social responsibility encompasses the economic, legal, ethical, and discretionary (philanthropic) expectations that society has of organizations at a given point in time”.
-Archie Carroll
OBJECTIVES
This article focuses on CSR growth and top corporate spending in India.
The purpose of this article is to analyse the current legal framework of CSR in India and identify CSR efforts internationally.
The purpose of this article is to: –
1) To know the CSR expenditure of Indian companies.
2) Analysis of domestic and international efforts regarding CSR.
HISTORY AND ORIGIN
Corporate Social Obligation (CSR) in India has a rich history and has developed over the long run. The idea of CSR can be followed back to old Indian practices of altruism and giving, where well off people and organizations were supposed to add to the government assistance of society.
In the advanced setting, the formalization of CSR in India started with the presentation of the companies Act, 2013. This law made it a legal requirement for some businesses to devote a portion of their profits to CSR initiatives.
The demonstration characterized CSR as the obligation of organizations to guarantee economical improvement while thinking about the interests of partners and society at large.
According to the Companies Act of 2013, eligible businesses are required to devote at least 2% of their average net profits from the three previous financial years to CSR initiatives.
These exercises incorporate yet are not restricted to killing appetite and destitution, advancing schooling, orientation fairness, and ecological supportability.
A significant turning point in the development of CSR in India occurred with the passage of this legislation. It achieved a shift from intentional CSR drives to a more organized and required approach. The demonstration additionally settled announcing prerequisites, making it important for organizations to reveal their CSR exercises in their yearly reports.
Since the execution of the companies Act, 2013, CSR in India has picked up speed. Many companies have embraced CSR as an essential piece of their business technique, perceiving the significance of adding to society and economical turn of events. Banking, manufacturing, and information technology are just a few of the industries that have actively participated in CSR initiatives.
Moreover, the Indian government has been effectively advancing CSR through different drives and missions. In order to maximize the impact of CSR efforts, it has encouraged collaboration between businesses, NGOs, and government agencies. The public authority has likewise settled the Public CSR Entryway, which fills in as a stage for organizations to exhibit their CSR exercises and offer prescribed procedures.
All in all, the set of experiences and beginning of CSR in India can be followed back to antiquated customs of generosity. Notwithstanding, the formalization of CSR as a lawful necessity started with the Companies Act, 2013. Since then, corporate social responsibility (CSR) has gained prominence in India, with businesses actively participating in a variety of social and environmental initiatives to support sustainable development and the welfare of society.
LEGAL FRAMEWORK OF CSR IN INDIA
The Companies Act
The consideration of CSR commitments in the Companies Act 2013 is an endeavour to supplement the public authority’s endeavours to impartially profit from development and remember the business local area for the country’s advancement plan. Indian companies follow Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 while undertaking CSR exercises.
Section 135[1]
Section 135 of the Companies Act 2013 sets out that:
1) A CSR Committee of the Board, comprised of three or more directors, one of whom will be an independent director, shall be established by businesses that have a net worth of 500 crore INR or more, an annual turnover of 1,000 crore INR, or a net profit of five crore INR or more.
2) It will be the duty of the CSR Committee to:
i. create and recommend a Corporate Social Responsibility Policy to the Board that outlines the company’s activities in accordance with Schedule VII;
ii. prescribe how much consumption to be caused on the exercises alluded to in I.; furthermore,
iii. keep a close eye on the company’s CSR policy on a regular basis.
3) The Leading body of each and every company will:
i. in the wake of considering the suggestions made by the Corporate Social responsibility Council, endorse the Corporate Social responsibility Strategy for the company and reveal items in such Arrangement in its report and put it on the organization’s site, if any, in such way as might be recommended; and
ii. guarantee that the exercises as are remembered for Corporate Social responsibility Strategy of the organization are attempted by the organization.
4) The Board is also responsible for ensuring that the company spends 2% of its average net profits from the previous three fiscal years on CSR and gives priority to the local communities in which it operates.
5) If the organization neglects to spend the sum, the Board in its report will determine the explanations behind not spending something similar.
CSR Rules, 2014
Companies Act Notification 2014, a set of rules under Section 135 of the Companies Act, came into force on April 1, 2014. It has established the following rules.
CSR activities
- CSR activities carried out by companies are based on established CSR policies, and activities carried out by companies in the course of their normal business activities are not covered by CSR activities.
Companies must carry out CSR activities approved by a CSR committee, either by themselves or through a charitable foundation established by the company to promote this effort, or by demonstrating that they have been involved in such activities for at least three years. This can be done through an independently registered charity. or in cooperation with other companies.
- The activities carried out in India are seen as just a part of CSR activities.
- Spending on activities that benefit only the company’s employees (also known as self-serving spending) is not considered CSR spending. Enterprises are free to spend funds on employee development, but their spending must not exceed 5% of their total CSR spending in a given year.
- Donations to political parties are also not considered CSR activities.[2]
LEADING COMPANIES SPENDING AND CASE STUDY
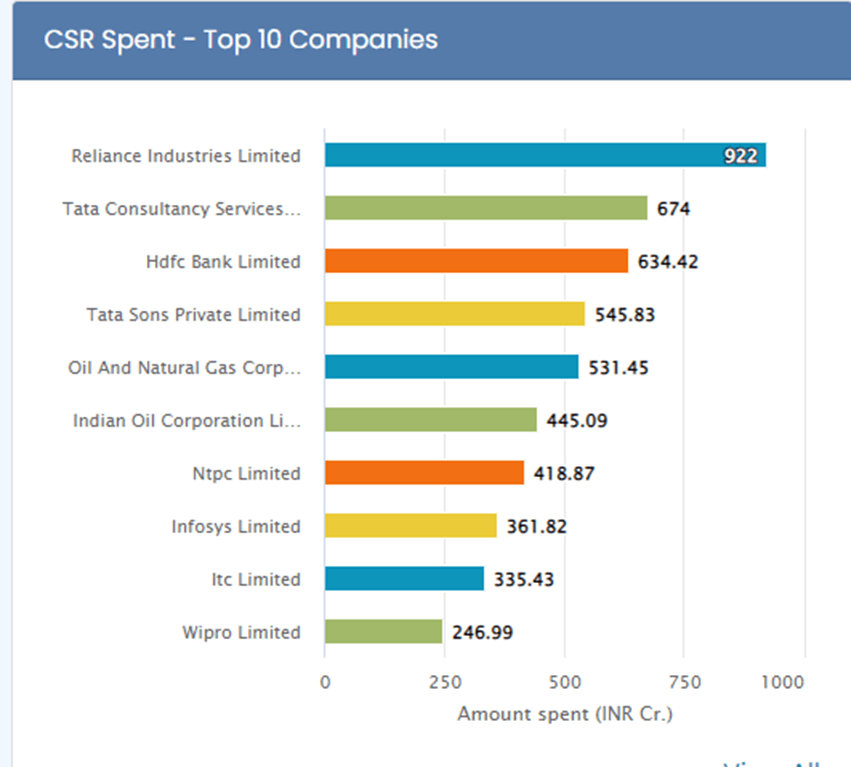
The above chart shows the CSR spendings by leading companies in India. This is taken from national CSR portal.
Reliance Industries Limited
Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) spent Rs. 922 crores on CSR drives in FY 20-21. The organization has been embraced the majority of its CSR drives through Dependence Establishment as it were. During the monetary year, the organization has burned through 49% of its spending plan for the advancement of training through grants and foundation acquirement.
Alongside schooling, the organization additionally centred around the advancement of medical care, rustic turn of events, sports advancement, and natural supportability.
The organization’s CSR use portfolio was as per the following Rs. 116 Cr. for medical services, Rs. 444 Cr. for schooling, Rs. 192 Cr. for Coronavirus help exercises, Rs. 42 Cr. for the improvement of livelihoods and Rs. 49 Cr. for sports advancement.
Tata Consultancy Services Limited
Tata Consultancy Services Limited TCS has spent Rs. 674 crores on CSR in FY 20-21. As a CSR drive, the organization contributed Rs.256 crores to the PM Really focuses Asset on battling Coronavirus. They likewise assisted in furnishing a Quarantine with focusing, supply of sanitizer and food parcels during the Coronavirus pandemic.
Aside from these, the organization has added to training advancement, medical services, workmanship and culture advancement, and Extension IT-a young business venture program. The organization’s significant use, other than PM Cares, was Rs. 13 Cr. for training, Rs. 17 Cr. for COVID aid efforts, Rs. 5 Cr. for medical care, and Rs. 5 Cr. for projects that help the community.
HDFC Bank Limited
HDFC Bank contributed Rs. 634.91 crores were spent on CSR in FY 20-21, more than the Rs. 627.86 crores. The organization has added to 200+ activities for CSR in the last monetary year.
Out of Rs. Rs. 634.91 crores financial literacy programs were financed with 233.31 crores. The bank prioritized education, rural development, healthcare, and COVID relief throughout the fiscal year.
The organization spent Rs. 140 Cr. for all encompassing country advancement, Rs. 100.97 Cr. for Coronavirus alleviation exercises, Rs. 47.31 for instruction, Rs. 17.79 for farmer’s livelihood, Rs. 16.78 for expertise improvement and Rs. 7 Cr. for entrepreneurial programs and startups.
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited
Oil And Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC) has spent Rs. 552.98 crores in FY 20-21 on CSR. In the pandemic time, the organization contributed Rs. 300 crores to PM CARES Asset to battle against Coronavirus. The remainder of the sum is spent on rustic turn of events, training advancement, climate, medical care, and sports. Other than PM Cares, the organization spent Rs. 57Cr. Rs. for education 31 Cr. for provincial turn of events, Rs. 21 Cr. for medical care, and INR 4.6 Cr. for promoting sports.
Indian Oil Corporation Limited
Indian Oil Corporation Limited (Indian Oil) is the country’s biggest coordinated and expanded energy organization. As a dependable enterprise, the organization has spent Rs. 460.38 crores on CSR in the last monetary year 20-21, Rs. 118 crores higher than the recommended sum. Out of Rs. 460 crores, Rs. 225 crores were added to PM Really focuses Asset on the Coronavirus pandemic.
The organization has likewise centred around medical services, public legacy protections, and training advancement. The organization contributed INR 30.9 Cr. Rs. for education 24 Cr. for ability improvement program, Rs. 16 Cr. for maintainability drives and INR 13 Cr. for COVID-related relief efforts.
NTPC Limited
NTPC Limited is an Indian legal organization, under the responsibility for Service of Force. It has spent a measure of Rs. 418.87 crores on CSR drives in FY 20-21, outperforming the recommended measure of Rs. 278.57.
The promotion and infrastructure of healthcare represent 66% of the company’s CSR budget. Moreover, they have added to provincial turn of events, climate manageability, sports, schooling advancement and catastrophe the board.
The organization is Setting up 50 Sterile Napkin Smaller than expected Assembling units (MMU) in the territory of Odisha under the “Stree Swabhiman” program. Clean napkin producing units are set up at NTPC Sipat, Ramagundam, Tanda, Vindhyachal and Farakka. The item is appropriated liberated from cost to the young adult young ladies of Govt. schools. In excess of 200 ladies have been conferred preparing in different professional courses like sewing, cosmetologist, food handling, and so on during the year for self-employability. Tool stash and sewing machines were given to the effective learners.
In conclusion, the business spent Rs. 64 Cr. for schooling, Rs. 33 Cr. for Rs. and the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan 31 Cr. for rustic advancement projects.
ITC Limited
ITC Limited ITC has a conviction that an organization’s presentation should be estimated by its Triple Main concern commitment to building financial, social, and natural capital towards improving cultural supportability.
In the last monetary year, the organization developed 640 Individual Family Latrines in 28 regions of 15 states in a joint effort with the separate State Legislatures/Locale sterilization divisions taking the all out to 38,153 IHHTs built such a long way in the Organization’s catchment regions. What’s more, 23 local area latrines were built/revamped in West Bengal and Tamil Nadu in the year, taking the aggregate all out to 104 local area latrines. Alongside sterilization framework advancement, unique centre was given to mindfulness missions to spur interest and drive social change.
The organization has imported 24 cryogenic holders of 20 tons each in a joint effort with Linde India Restricted to facilitate the bottlenecks in shipping oxygen.
They made contribution to the PM CARES Fund. 100 crores for the Coronavirus pandemic. It upheld the calamity impacted individuals by its alleviation program and contributed Rs. 54.32 crores.
Infosys Limited
In FY 20-21, Infosys Limited spent Rs. 325.32 crores on its CSR drives. The Infosys Foundation is the sole channel through which the company has been carrying out its CSR initiatives.
In the last monetary year, the organization took different drives for battling the Coronavirus pandemic by giving fundamental clinical gear and framework to different medical clinics and bleeding edge labourers, supporting everyday occupation prerequisites of poor people and penniless. The alleviation work, which started with setting up of Coronavirus selective clinics and wards, supply of clinical gear, PPE packs, and sanitizers proceeded with skillet India through 2020-21 and is proceeding with this year.
The IFA-Infosys Establishment association is supporting 11 tasks attempted by craftsmen, researchers, and educators, and empowering them to proceed with their work.
The organization has been proactively supporting ventures that help fighters and their families when they resign or are martyred.
In one such undertaking, the Establishment has assisted with building a Sainik Sadan for the Rajya Sainik Board, Odisha in Bhubaneswar. The Rajya Sainik Board, Odisha, which is under the managerial control of the Home Division, Legislature of Odisha, goes about as a nodal organization for planning and executing different government assistance proportions of the focal and state legislatures. The Board is focused on advancing government assistance measures for war widows, widows of ex-servicemen, The Second Great War veterans and their widows and wards from Odisha, and the groups of the serving troopers of Odisha. There are approximately 42,500 registered widows and ex-service members, and the total number of dependents exceeds 2,000.
Wipro Limited
Wipro Limited spent Rs. 251.19 crores on CSR drives in FY 20-21. The company contributed to education for the underprivileged in the most recent fiscal year. This program tends to a range of basic issues looked by impeded networks with regards to school training – beginning from enrolment in schools to nourishment for youngsters, directing administrations for guardians, therapeutic schooling, among others. These kids are from the absolute most weak gatherings in our general public – metropolitan ghettos, HIV-impacted families, transient work families, road youngsters. Also, they contributed towards Training for Youngsters with Incapacity.
The organization has a Local area Environment program. This undertaking in agroforestry in provincial Tamil Nadu helps ranchers in actually carrying out coordinated cultivating rehearses. Workers in the informal sector of waste benefit from comprehensive skills enhancement and social, nutritional, and health security through urban solid waste management (SWM) projects in Bengaluru and Mysore. Both the projects confronted functional difficulties because of the continuous pandemic. Various versatile measures were embraced, for example, the utilization of advanced stages for data sharing, preparing of staff and waste pickers, and changing to online accommodation of uses for federal retirement aide.
Power Grid Corporation of India Limited
Power Grid Corporation of India Limited is India’s biggest Electric Power Transmission Utility. It spent Rs. 240.59 on CSR in FY 20-21. The organization added to 270+ undertakings for its CSR drives. the organization took different drives for training, medical services, climate, disinfection, provincial turn of events, and workmanship and culture advancement.
Tata Steel limited
Tata Steel limited is one of the most beneficial and least expense makers of steel on the planet. Sustainability is an important part of doing business at Tata Steel. It is driven by the company’s leadership and has a governance structure that applies to the entire organization.
Through its Education Signature Program, the company has improved the lives of over 2,51,000 children. They had the option to contact 2,303 people through Sabal Place and different inability connected programs.
Altogether, the organization spent Rs. 221.98 crores in the most recent fiscal year (20-21) for its CSR initiatives.
ICICI Bank Limited
ICICI Bank Limited has been committed to corporate social responsibility (CSR) for a considerable amount of time. The Bank’s commitment to financial improvement incorporates a few spearheading intercessions, with an emphasis on gathering explicit objectives.
The bank has burned through Rs.200 crores in FY 20-21 for its CSR drives. During the year, they spent Rs. 71.38 crores for Coronavirus help. It contributed towards Ability improvement through ICICI Foundation for Abilities.[4]
NATIONAL CSR INITIATIVE
Presently Corporate Social responsibility (CSR) is all around acknowledged among investors as well similarly as with different partners of society in India. The term CSR is new typical for Indian associations. CSR will in general zero in on how is managed benefits after they are made. Larger businesses are aware that corporate social responsibility is an essential component of the business framework for sustainable development. Organizations likewise consider that CSR is a methodology towards Social Benefit manageable turn of events and spotlight on the triple primary concern of Monetary, Natural and Social execution.
In India, the term Corporate Social Obligation (CSR) is broadly being utilized despite the fact that connected ideas and terms, like business obligation, maintainable turn of events, magnanimity, maintainability, corporate citizenship, mindful business, triple primary concern, shared esteem, esteem creation, business morals, financial obligation, lower part of pyramid, partner the board, corporate obligation, and corporate social execution.
The key features of the National CSR Initiative in India are as follows: –
- Mandatory CSR Spending: As per the Companies Act, certain companies meeting specific financial criteria are required to spend at least 2% of their average net profits on CSR activities. This provision ensures that companies contribute towards social and environmental causes.
- Focus Areas: The initiative encourages companies to focus their CSR efforts on areas such as education, healthcare, poverty alleviation, environmental sustainability, and rural development. This helps address critical social issues and contribute to the overall development of the nation.
- Reporting and Compliance: Companies are required to report their CSR activities and expenditure in their annual reports, ensuring transparency and accountability. It helps track the impact of CSR initiatives and these reports are encourage companies to fulfil their obligations.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: The initiative promotes collaboration between companies, government agencies, and non-profit organizations to maximize the impact of CSR activities. Partnerships enable sharing of resources, expertise, and best practices, leading to more effective and sustainable outcomes!!
- Capacity Building: The initiative emphasizes the importance of building the capacity of companies to implement CSR effectively. It provides guidance, training, and resources to help companies develop robust CSR strategies, measure impact, and align their initiatives national development goals.
Ensuring the overall development of the nation, the CSR Initiative in India has played a crucial role in encouraging companies to contribute to social welfare and sustainable development. It has led to an increase in awareness and has implemented CSR practices across various sectors, positively impacting communities and the environment! By aligning business interests with societal needs, the initiative aims to create a more ^inclusive and responsible corporate sector in India.
The indicative activities, which can be undertaken by a company under CSR, have been specified under Schedule VII of the Act. The activities include:
- Eradicating extreme hunger and poverty,
- Promotion of education, gender equality and empowering women,
- Combating Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome and other diseases,
- Ensuring environmental sustainability;
- Contribution to the Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund or any other fund set up by the Central Government for socio-economic development and relief and funds for the welfare of the Scheduled Castes, the Scheduled Tribes, other backward classes, minorities and women etc.[5]
INTERNATIONAL CSR INITIATIVE
The Importance of International CSR Initiatives in India:
1. Addressing Social Challenges: India faces numerous social challenges, including poverty, education gaps, healthcare disparities, and gender inequality. International CSR initiatives provide much-needed support to tackle these issues by investing in education, healthcare infrastructure, skill development programs, and women empowerment initiatives.
2. Environmental Sustainability: India is grappling with environmental issues such as pollution, deforestation, and climate change. International CSR initiatives play a crucial role in promoting sustainable practices, renewable energy adoption, waste management, and conservation efforts. These initiatives contribute to India’s commitment to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
3. Economic Development: International CSR initiatives contribute to India’s economic growth by fostering entrepreneurship, supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and creating employment opportunities. By investing in local communities, these initiatives help uplift marginalized sections of society and promote inclusive growth.
4. Knowledge Sharing and Technology Transfer: International CSR initiatives often involve knowledge sharing and technology transfer, enabling Indian organizations to learn from global best practices. This exchange of ideas and expertise helps enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of local initiatives, leading to sustainable development outcomes.
Successful International CSR Initiatives in India:
1. The Coca-Cola Company:
Through its “Support My School” initiative, Coca-Cola has transformed over 1,000 schools in rural and semi-urban areas, providing access to clean drinking water, sanitation facilities, and sports infrastructure.
2. Microsoft:
Microsoft’s “Project Shiksha” aims to bridge the digital divide in India by providing computer education to under privileged students and training teachers in technology-enabled learning.
3. Unilever:
Unilever’s “Project Shakti” empowers rural women by training them as micro-entrepreneurs, enabling them to sell Unilever products in their communities and improve their livelihood.
CHALLENGES
1. Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging and managing the expectations of various stakeholders, such as employees, customers, communities, and investors, can be complex. It is crucial to identify and prioritize their needs and concerns.
2. Measurement and Reporting: Measuring the impact of CSR initiatives and reporting the results in a transparent and credible manner can be challenging. Developing appropriate metrics and standards is essential to demonstrate the value and progress of CSR efforts.
3. Integration into Business Strategy: Integrating CSR into the core business strategy can be challenge. It requires aligning CSR goals with the overall business objectives and ensuring that CSR initiatives are not seen as separate from the company’s core operations.
4. Resource Allocation: Allocating sufficient resources, both financial and human, to CSR initiatives can be a challenge. Balancing the short-term financial goals with long-term sustainability objectives is crucial for effective resource allocation.
RECOMMENDATIONS
1. Stakeholder Engagement: Actively engage with stakeholders to understand their expectations and involve them in the decision-making process. Regular communication and feedback mechanisms can help build trust and foster collaboration.
2. Goal Setting and Measurement: Setting clear and measurable goals for CSR initiatives, aligned with the company’s values and priorities.
3. Integration and Collaboration: Integrating CSR into the company’s overall strategy and operations. Foster collaboration across departments and functions to ensure that CSR is embedded throughout the organization.
4. Leadership Commitment: Demonstrate strong leadership commitment to CSR by allocating dedicated resources, establishing clear accountability, and promoting a culture of sustainability and social responsibility.
5. Partnerships and Collaboration: Collaboration with external stakeholders, such as NGOs, government agencies, and other businesses, to leverage their expertise and resources. Partnerships can enhance the impact and reach of CSR initiatives.
CONCLUSION
The CSR landscape in India is witnessing a paradigm shift, with leading companies really acknowledging the importance of responsible business practices. Overall, CSR in India has the potential to drive sustainable development and contribute to the country’s social and economic progress. With continued commitment, collaboration, and innovation, CSR can play a vital role in addressing societal challenges and creating a more inclusive and sustainable future for India. By focusing on both national, and international CSR initiatives, these companies are not only complying with legal mandates but also really contributing meaningfully to societal and environmental well-being on a global scale.
As the corporate world continues to evolve, the synergy between business success and social responsibility, will really play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable and equitable future.
“Businesses need to go beyond the interest of their companies to the communities they serve.”
Ratan Tata
REFERENCES
- https://csrbox.org/Impact/description/Article_full_Top-50-Companies-in-CSR-Activities-Funding-in-India_36
- CSR: Corporate Social Responsibility – ClearIAS
- Unit-9.pdf (egyankosh.ac.in)
- Home (csr.gov.in)
- https://www.csr.gov.in/content/csr/global/master/home/home.html
- https://indiacsr.in/corporate-social-responsibility-csr-in-india/#google_vignette
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/andhra-pradesh/csr-initiative-to-teach-children-importance-of-source-segregation-of-waste/article67669358.ece
- https://www.livemint.com/economy/indias-services-growth-at-three-month-high-in-december-11704436508697.html
- https://csrbox.org/media/CSRBOX-India-CSR-Outlook-Report-2022_Full-version.pdf
- https://www.ril.com/about/corporate-social-responsibility
- https://www.iisd.org/system/files?file=publications/csr_guide.pdf
- International Corporate Social Responsibility (ICSR) | Business.gov.nl
- Home (mca.gov.in)
- Seema g. sharma, corporate social responsibility in India: an overview,43 INT’L L. 1515 (2009)
- Mark S. Schwartz and Archie B. Carroll,13 BEQ, 503 (2003)
- The Companies Act,2013, § 135, No. 10, Acts of Parliament,2013 (India)
[1] https://www.mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/CompaniesAct2013.pdf
[2] Unit-9.pdf (egyankosh.ac.in)
[5] CSR: Corporate Social Responsibility – ClearIAS
Disclaimer: The materials provided herein are intended solely for informational purposes. Accessing or using the site or the materials does not establish an attorney-client relationship. The information presented on this site is not to be construed as legal or professional advice, and it should not be relied upon for such purposes or used as a substitute for advice from a licensed attorney in your state. Additionally, the viewpoint presented by the author is of a personal nature.




0 Comments