
This article is written by Supriya of S.S Khanna Girls’ Degree College, University of Allahabad
Abstract–
Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the inventions that are literary and artistic works, symbols, names and images. Intellectual property rights are like any other property right. They allow creators, or owners, of patents, trademarks or copyrighted works to benefit from their own work or investment in a creation. These rights are outlined in Article 27 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which provides for the right to benefit from the protection of moral and material interests. This PR provide certain exclusive rights to the inventors or creators of that property, in order to enable them to reap commercial benefits from their creative efforts or reputation. There are several types of intellectual property protection like patent, copyright, trademark, etc. The IP rights not only help individuals keep their intellectual property safe but also provide them with various ways in which they can use their intellectual property to expand their business without having to worry about the concept being copied or stolen.
Introduction –
Intellectual property is an intangible aspect dealing with creation of human minds originating or developing from ideas and expression. Intellectual Property Rights defined as-“Intangible property that is the result of creativity”. So, the word Intellectual denotes the works produce as a recent of creativity. When we say intangible aspects, it simply means it cannot be seen or felt. It is the product of human imagination, creativity and inventiveness. These creations are intangible that it cannot be seen it becomes necessary to protect the inventors or creators’ invention or creation and also appreciate and recognize their efforts. Hence, a set of rights provided to protect the Moral and legal interest of such inventors or creators and this form the discipline of intellectual property rights. It protects genuine business assets and invention or creation for a limited time as provided under the different IP laws and IPR helps monetize the IP.
Why do we need to have this Intellectual Property protected-
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights UDHR refers to Intellectual Property Rights under Article-27 that states that “Everyone has the right to the protection of the Moral and material interest resulting from any scientific, literary or artistic production of which he is the author”. We know that hard work is making a business successful in good direction. IPR are one of the ways to protect and reap the benefits from that hard work for the long term.
Different ways to protect your Intellectual property: we have to be aware of your Intellectual property rights, consult an expert, keep it under security, hire an auditor and protect your IP without delay. There are four types of Intellectual property to protect your idea-
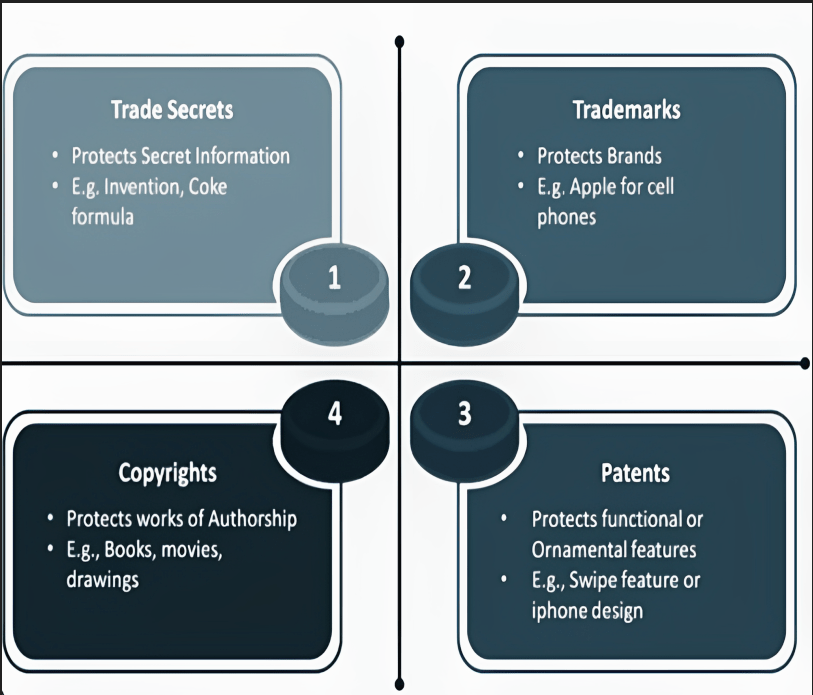
1.Trade secrets –
Trade secrets are the type of Ip and a plan or action to protect the Ip. It is a process, plan, formula or method to a manufacturer, which gives it an advantage over competitors. It is confidential information that has a commercial value attached to it and reasonable steps have been taken to keep it a secret for as long as possible. It gives in the industrial economy cause of main two reasons that are other forms of Ip like patent, trademark, and copyright have an element of Uncertainty and other reason is trade secrets have gained importance is changing to so rapidly that if has exceed the existing laws intended to encourage and protect inventions or creation. There is no bureaucratic delay and non-multiyear waits for grant from the government of India. Trade secrets start upon the creation of ideas in some concrete form, and continue as long as secrecy is maintained. There is no statute or legislation for registration that governs the protection of trade secrets in India but trade secrets are enforced contract law principle of equity or by way of common law action for breach of confidence.
Examples of trade secrets include:
- Soda formulas
- Customer lists
- Survey results
- Computer algorithms
Unlike the other types of intellectual property, you can’t obtain protection by registering your trade secret. Instead, protection lasts only as long as you take the necessary steps to control disclosure and use of the information.
2.Trademarks
Trademark is a world phrase symbol, design or combination of it that distinguishes your product from somebody else’s. So, basically, we are able to identify a particular goods or service by associating that goods or services to that offer the branding belonging to a particular company. When a business becomes successful it paves way of copy cut selling of product illegally and it may damage the reputation of the brand due to this reason the trademark reflects the reputation of the business and becomes most valuable asset of the business because it is used as a marketing tool as a way of labeling and hence, protecting trademark come up crucial for a business. Registration of trademarks like other IP also establish ownership and it makes it easy to enforce their right against any infringes or any third party using it without authorization of the owner due to this trademark is to be registered. Under the Trademark Act in India, it must have been non – generate and not be descriptive of the services of the goods that they are providing and it Must not be identical or similar to some marks that are already existing. The validity of protection of a trademark is for ten years and it can be perpetually renewed for the period of 10 years. So, legal protection of the owner to control who uses their trademark and it ensures the Genuity of the product they are purchasing. To register a trademark, you can:
- File a “use” application after using the mark.
- File an “intent to use” application before using the mark.
- If a foreign application exists, a trademark holder might be able to rely on that application for use in the United States. Filing an application is complex, so most applicants hire an attorney who specializes in trademarks.
3. Copyrights –
Copyright is a legal right providing exclusive authority over the creator’s work including distribution and use of the work. Copyright is grant to protect literary, artistic, musical and dramatic works, sound recordings etc. and it also protect the interest to those who are interested to such copyright work like performing artist in performances, producers’ phonograms and their recordings and those of broadcaster in their radio and television programmes and it also cover software databases as well. Copyright does not protect ideas; it protects the expressions. It ensures the economic right to derive financial reward from the use of their works by others. Apart from the economic right, copyright ensures the moral right. It ensures work of the creator that is created or attributed to the original author and prevents from being altered or their link with their work. The artistic validation of copyright in India is lifetime in addition to sixteen years and sixty years for the musical, sound recordings, and dramatic work. Registration is not mandatory in copyright but if anyone wants to enforce their right against any unlawful or unauthorized use of the original work then registration is done in accordance with the Copyright Act, 1957 and become a legal owner of their creative work in respect of books, paintings, music, video, paintings, website, mobile application etc. In order to qualify under copyright laws, the work must be fixed in a tangible medium of expression, such as words on a piece of paper or music notes written on a sheet. A copyright exists from the moment the work gets created, so registration is voluntary.
However, registered works may be eligible for statutory damages and attorney’s fees in a copyright infringement suit, so you may want to consider registering your work through the U.S. Copyright Office. You can register your copyright online by completing an application, submitting a nonrefundable fee of $35, and sending in a nonreturnable copy of your work.
4.Patents –
patent is an exclusive right granted for the public disclosure of an inventor process or product and to protect their technical invention. This right provides exclusive right to the person or the inventor to manufacture huge and sell their invention and exploit others from doing the same and, if anyone infringes or use it unauthorizedly then owner can also stop and claims for damages from them but this right to monopoly is limited only for twenty years and after the expiration of the term of protection the subject inventor enters the public domain for any third party to use it commercially or otherwise. Patent Act 1970 deals with protection of and registration of patents in India. Three main criteria of Patent are the invention relating to a product of process is new or should be novel meaning that it should not be known to public and it should have inventiveness that they should be some technical advancement or an inventive step that is not obvious and the other criteria is that the patent should have Industrial practibility. Term of patents are short in India and there is no worldwide protection. Internationally there are two ways by the Paris ijhat owner get to enjoy commercially exploitation for a limited period that is twenty years including, making, using, selling, and unauthorized use or selling of the same would infringement and the patency of the owner of the third particular invention can stop unauthorized used on sell or damage for loss of monetary benefits that is rightfully to the owner patents.
You’ll discover three types of patents:
- Utility
- Design
- Plant
A utility patent is the most common type, covering any process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvements thereof.
To qualify for a utility patent, the invention must be novel, nonobvious, and have some usefulness. Novel means new and not known by anyone else, while nonobvious means that it can’t be immediately obvious to someone having ordinary skills in the industry. A design patent covers any new, original, and ornamental design for an article of manufacture, while a plant patent covers any new variety of asexually produced plant. A design patent lasts for 14 years, and a utility or plant patent lasts for 20 years.
Conclusion –
The protection of IP is important as it not only enables the owner to commercially exploit his work that also stops unauthorized use or unlawful use and claims in damage for loss and hardship including monetary loss. Intellectual property rights are growing day by day. These rights prevent the creations & invention of owner. In all intellectual property rights copyrights, patent & trademarks are more prevailing rights. We can say that when the existence of the IPR the inferior or copying work is not fit.
References-
1.https://www.abounaja.com/blogs/importance-of-intellectual-property-protection
2.https://vakilsearch.com/blog/5-reasons-why-patent-is-important-for-businesses/
3.https://henrygoh.com/top-10-reasons-why-a-patent-is-important/




0 Comments